Pedaling Past Injury
Cycling is a growing activity. A recent survey revealed that more than 100 million Americans ride a bike each year. This includes those who ride recreationally, for exercise, as a means of transportation to work or school and who complete in cycling competitions. US Dept of Interior survey shows the bicycling is the third most popular participatory sport, after swimming and general exercise.
The bicycle was invented in the early 1800’s by Baron Karl von Drais in Germany in response to widespread starvation and the slaughtering of horses – consequences of crop failures the year before. The vehicle called a “velocipede” was propelled by pushing off the ground with the feet.
In 1890 mass production of bicycles began with the introduction of the chain drive, front or rear suspensions and pneumatic tires.
Studies show that a third of bicyclists will fall off their bike. It makes common sense to think about learning how to fall off the bike.Part of the technique involves rolling or sliding during a fall. It may result in some loss of skin, however, it allows a rider to return to the bike much sooner than if a fall results in broken bones.
Cyclists can face many problems ranging from acute injuries to chronic injuries including bursitis, muscle strains, and nerve compression; to postural intolerances including neck, shoulder and back pain.
Any chronic or postural intolerance should first be evaluated with the rider’s position on the bicycle. If one experiences pain only when riding and not off the bike an evaluation of bike posture needs to be completed. Once an adjustment of the bicycle position or change of equipment is made proper exercises should be initiated. If the same pain is present off the bike an assessment of the cause of the pain needs to be done.
Pedaling Past Injury by decreasing back pain…
Overuse injuries are quite common with cyclists, due to many factors, primarily due to poor core pelvic stabilization along with poor flexibility of the trunk and lower extremities. Cycling places one into a negative position of the trunk for long periods of time depending on the distance traveled.
One of the best ways to avoid these problems is having a seat that fits well: the seat is the proper height and width and aligned properly. Reaching the handlebars should not cause neck and back pain. If pain is there it is a bike fit problem.
Limited motion in the trunk and lower extremities needs to be addressed otherwise the pain will continue and possibly increase in intensity and severity.
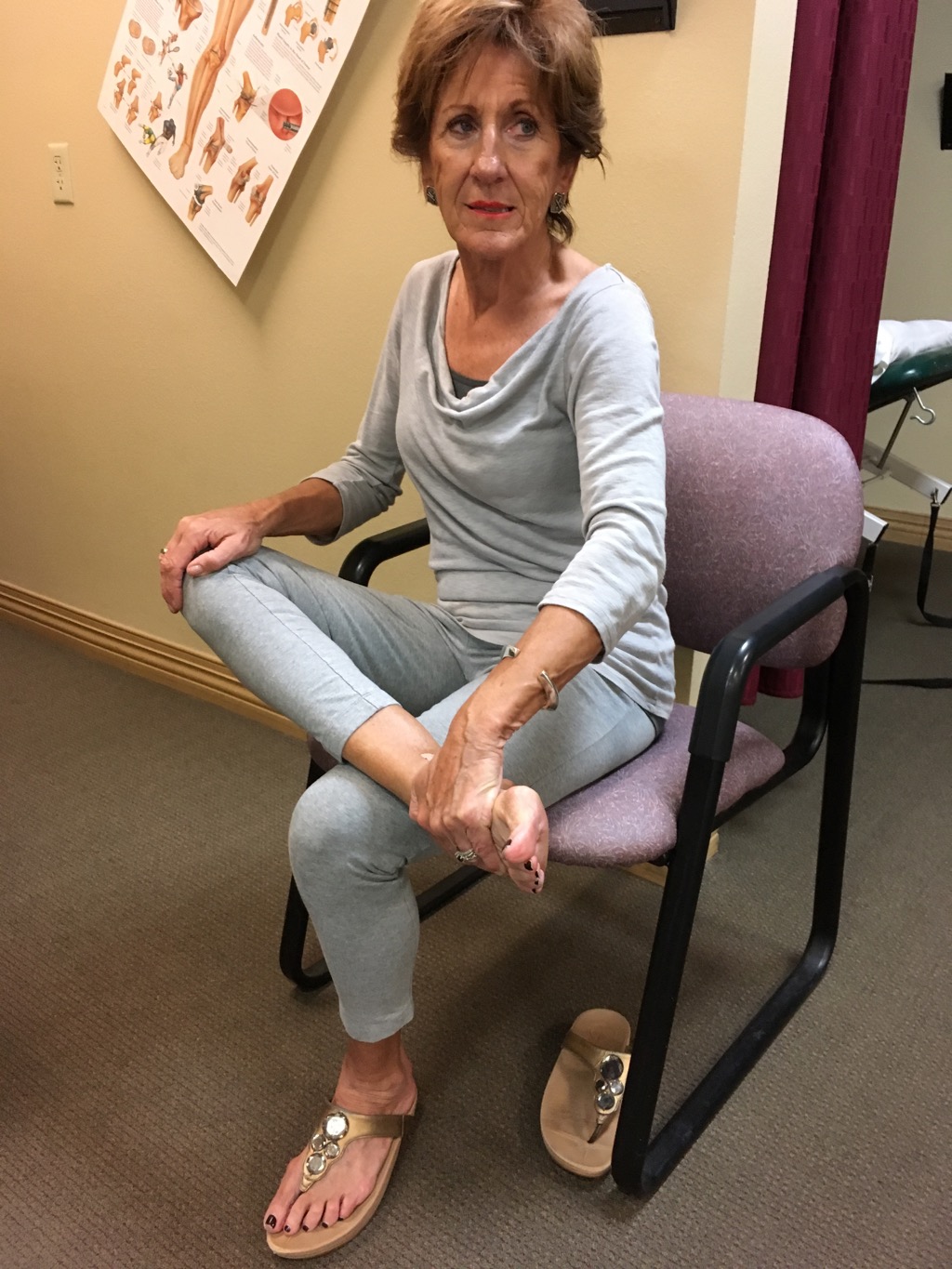
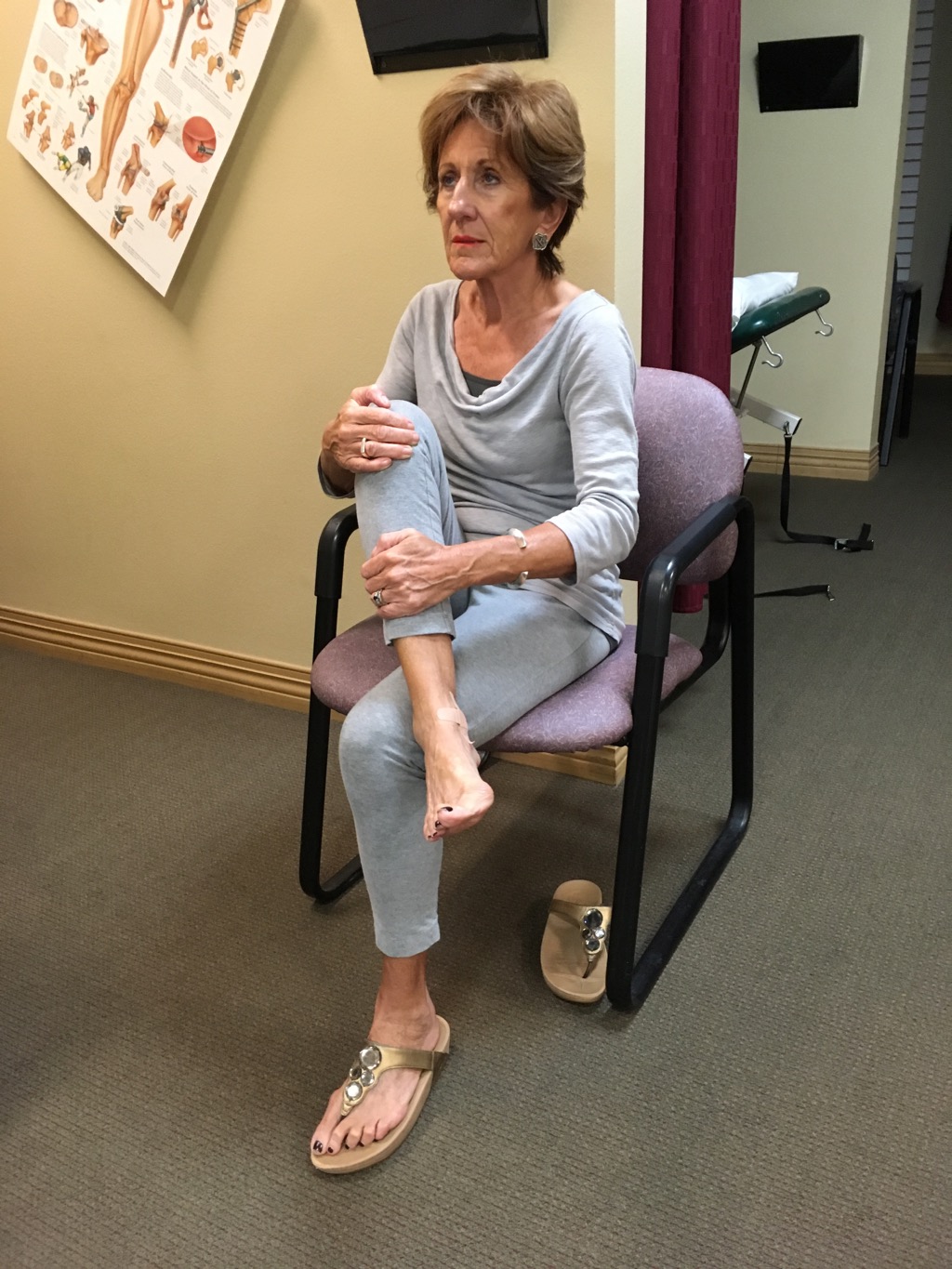
Sit in chair and bend forward at waist keeping the back straight with head on shoulders not the chest. Cross one leg over the other with the ankle above the knee. Pull up on the ankle and push down on the knee. Hold for 30 seconds. Alternate and change legs repeat for 30 seconds.Repeat 3 reps alternating legs.
Sit in chair and bend forward at waist keeping the back straight with head on shoulders not the chest. Cross one leg over the other with the ankle above the knee. Grasp the leg with both hands and pull the crossed knee to the opposite shoulder. Hold for 30 seconds. Alternate and change legs repeat for 30 seconds. Repeat 3 reps alternating legs.
Go to website: www.pilatesplusforboomers.comGo to low back pain exercises under Pilates plus exercise programs.
Continue with the stretching exercises until pain starts to subside, then initiate strengthening exercises. If no change in low back pain for 3-4 weeks, consider seeking medical evaluation and Physical Therapy.
Pedaling Past Injury by Controlling the Core
 Low back and neck pain is a common complaint of cyclists. Getting the core muscles under control is of the utmost importance as it has overall value with our daily activities
Low back and neck pain is a common complaint of cyclists. Getting the core muscles under control is of the utmost importance as it has overall value with our daily activities
- Muscles of the trunk and torso stabilize the spine from the pelvis to the neck and shoulders, allowing the transfer of powerful movements of the arms and legs.
- All powerful movement originates from the center of the body outward, not from the limbs alone.
- Before any powerful rapid muscle contractions can occur in the limbs, the spine must be solid and stable, the more stable the core, the more powerful the extremities can connect.
- Training the core muscles also corrects postural imbalances that can lead to injuries.
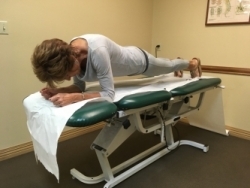
Plank Exercises are excellent exercises to strengthen the core muscles.
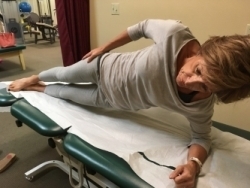
For additional exercises and directions on completing the exercises go to https://pilatesplusforboomers.com/level-2-golf-exercises/
Pedaling Past Injury by maintaining proper knee mobility & strength
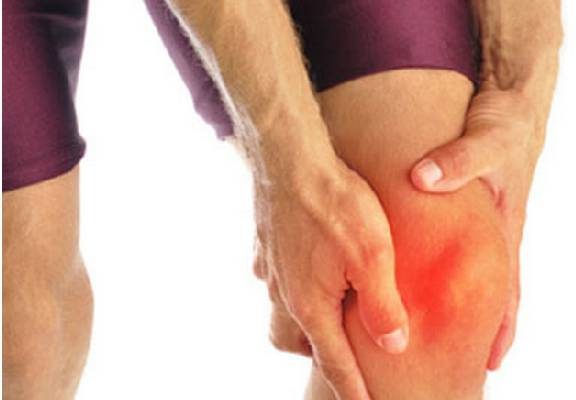
Knee injuries can be the demise of cyclists as well as anyone involved in athletic/recreational activities. The knee is vulnerable to injury as it is “struck” between the foot and hips, both of which are affixed to the bike. If the foot is turned in or out, unable to move naturally, the tibia will rotate and put stress on the knee. If the seat is set incorrectly..to high, low,far forward or far back..the hips can be forced to tilt forward, backward,left or right. The femur is forced to adjust, again adding stress to the knee.
Patellofemoral pain is typically caused by the patella tracking to far lateral and rubbing outside its groove on the femur, leading to inflammation and pain.
Proper strengthening will reduce the muscle imbalances leading to knee injuries. One method is to evaluate the knee strength in relation to body weight. The closer the strength is to body weight the risk of injury becomes reduced. One excellent method of testing the strength is with Isokinetic testing using a Biodex or Cybex isokinetic machine. Several Physical Therapy clinics in the area have the machine.
When a health care professional evaluates the knee, make certain the hips and ankles are evaluated also, for limited motion or strength deficits.
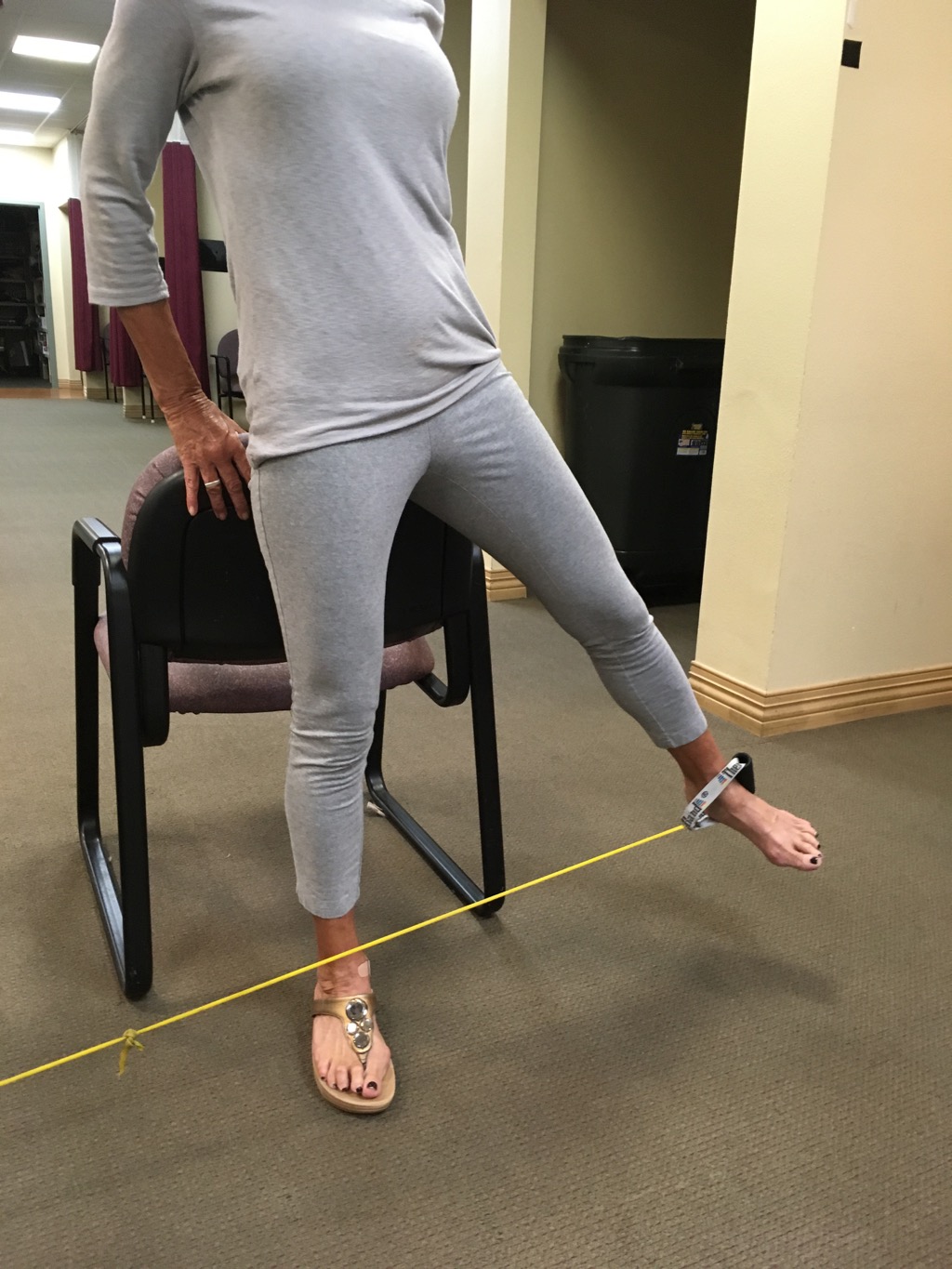
A good strengthening exercise is to use therapeutic tubing and/or a weighted cable machine to strengthen hips/knees.. Go to:
www.pilatesplusforboomers.com & click on “knee exercises and treatment”.
Level 2 Strengthening Knee & Hip musculature
Attach one end of tubing to table leg or object that will not move. Place
chair next to you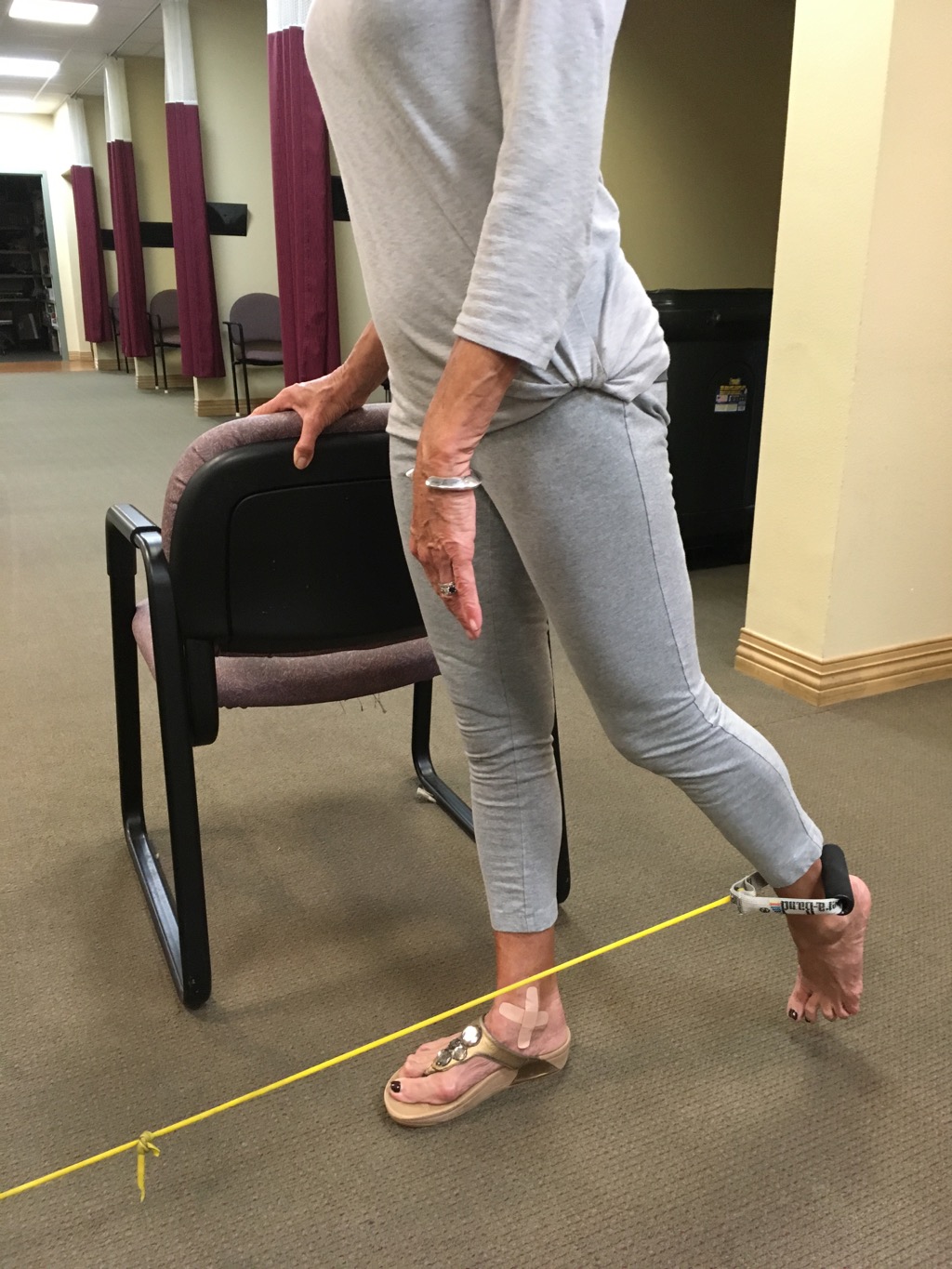 to hold on to chair for balance. Stand erect move leg in 4 different directions. Each time you move the leg against resistance breathing out and pull the belly button to the spine, breathing out for 5 seconds and breathe in 5 seconds when relaxing taking the leg back to the original position.
to hold on to chair for balance. Stand erect move leg in 4 different directions. Each time you move the leg against resistance breathing out and pull the belly button to the spine, breathing out for 5 seconds and breathe in 5 seconds when relaxing taking the leg back to the original position.
ISOKINETIC TESTING !! Maintaining knee strength to body weight ratios!!
Part of a Physical Therapy knee evaluation should consist of isokinetic testing to determine the quadriceps knee strength in relation to body weight (should be 80% or better of body weight). Also, the strength relationship of hamstrings to quadriceps
Isokinetic exercise is a type of strength training. It uses specialized exercise machines that produce a constant speed no matter how much effort you expend. These machines control the pace of an exercise by fluctuating resistance throughout your range of motion. Your speed remains consistent despite how much force you exert.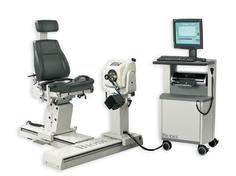
You can adjust the target exercise speed and range of motion to suit your needs. Different attachments on the machines can isolate and target specific muscle groups. You can use Isokinetic exercise to test and improve your muscular strength and endurance .
If the Physical Therapist is unable to complete an evaluation with isokinetic machine, recommend finding one that can complete the test. Lake Center for Rehab 910 Old Camp Rd Sumter Landing has an Isokinetic testing machine. Determining knee strength in relation to body weight is key to any knee strengthening program.
PROPER HYDRATION CRITICAL WHEN PARTICIPATING IN RECREATION ACTIVITIES, ESPECIALLY WHEN OUT DOORS!!
Dehydration occurs when you lose more water via sweat and urine than you’ve taken in, can be especially dangerous for older adults. A lack of sufficient fluid in the body can temporarily cause confusion and put you at risk for falls.
Dehydration can be challenging to detect as we age because classic signs such as dry mouth, thirst, fatigue and skin that doesn’t spring back quickly when pinched can also be caused by other factors. A 2015 review of research by the independent Cochrane Collaboration found that there was no one reliable test for dehydration.
How much – and what – should you drink? There is really no rule, that’s appropriate, can vary a great bit from person to person. The heavier, taller, and more active you are the more fluids you need to take in to cover your losses.
Drink before you feel parched. By the time you feel thirsty, you might be dehydrated.
Sip small amounts throughout the day. Carrying a water bottle with you can help remind you to drink.
Include other beverages and foods. All beverages(other than alcoholic drinks) will hydrate you, and that includes caffeinated drinks. Coffee and tea are mild diuretics, they can cause you to urinate more. But they will add more to your liquid stores than you will lose. Soups, fruits and vegetables are also good sources of liquid.
Take your health into consideration. Ask your doctor whether medical conditions you have or medications you take affect your hydration needs.
A 2016 study in the Annals of Family Medicine found that obese people were more likely to be inadequately hydrated as well. Having dementia, Parkinson’s disease or a stroke can also increase the chance of dehydration.
Florida with its high temps/humidity increase the risk for all to be dehydrated…Play it safe…stay hydrated.