Spinal stenosis is a condition that occurs as the spinal canal narrows, restricting or compressing the nerve roots and spinal cord. It is often caused by osteoarthritis of the spinal column. Common symptoms are pain in the legs or lower back when standing or walking.
The narrowing of the spinal canal often happens in the lower back (lumbar spine) and neck (cervical spine) or, on rare occasion, the thoracic region of the spine (upper back).The symptoms of pain, weakness, or numbness can occur in several areas, depending on the region of the spinal cord that is being pinched.
Causes
Spinal stenosis can be a congenital condition, with some people having a narrow spinal canal from birth. But more often, it results from degenerative changes in the spine, the wear and tear that leads to osteoarthritis. Bony overgrowth from osteoarthritis, thickening of a ligament in the back, and bulging discs can contribute to the condition. If you are over age 50, you have a risk of spinal stenosis. Women are more at risk than men.
Other conditions that can cause spinal stenosis include inflammatory spondyloarthritis, spinal tumors, trauma. Your risks are increased if you had a previous spinal injury or surgery on your spine.
Symptoms
People who have lumbar spinal stenosis often have pain in their legs and lower back after walking
The pain subsides after sitting down or leaning over. In cases of cervical spinal stenosis, patients can have symptoms similar to lumbar stenosis but with prominent neck pain and peculiar sensations in the arms, poor leg function, or incontinence. There also can be numbness, weakness, or cramping of the legs.
Diagnosis
Spinal stenosis can be diagnosed by a history and physical examination, but imaging studies (X-rays, CT scan, MRI) often are used to evaluate causes and severity of the disease. You might also have an electromyogram (EMG) performed to check the function of the nerves in your legs. Blood tests will be done to check for other conditions you may have and rule out other possibilities.
Treatment
There are several different types of treatment, other than surgery. However, many physicians lead patient’s to think surgery is the answer. If you are told other methods will not work and the best is surgery, get at least a second opinion, someone away from The Villages.
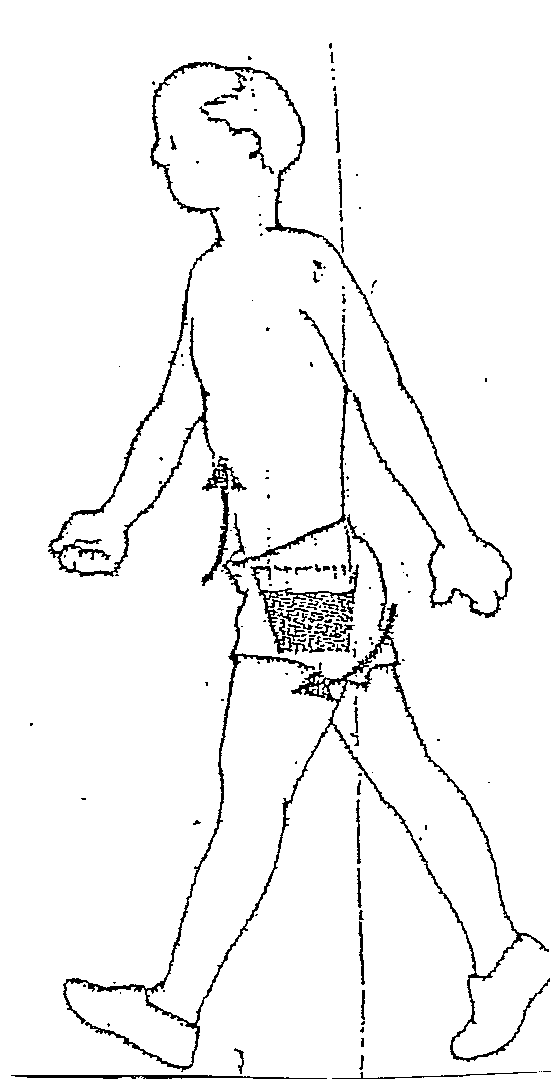
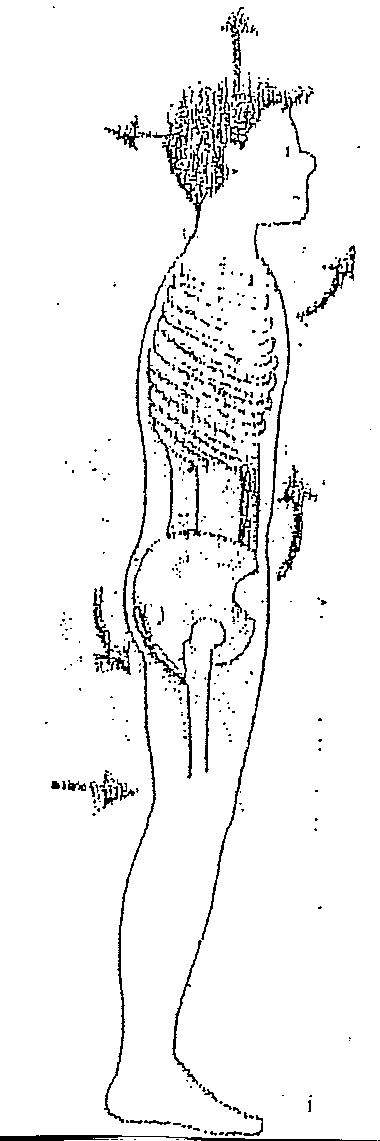 Physical Therapy is being used more and more with success, however, many do not emphasize core stabilizing exercises.
Physical Therapy is being used more and more with success, however, many do not emphasize core stabilizing exercises.
Exercise can help reduce pain and numbness, it will not cure the stenosis.
Strengthening and lengthening muscles involved in the spine are primarily core muscles. Improving posture is the most important. Most of us have poor posture. We need to keep our head on our shoulders, not on our chest. We need to pull the belly button up and back to the spine. This needs to be practiced throughout the day, every day.
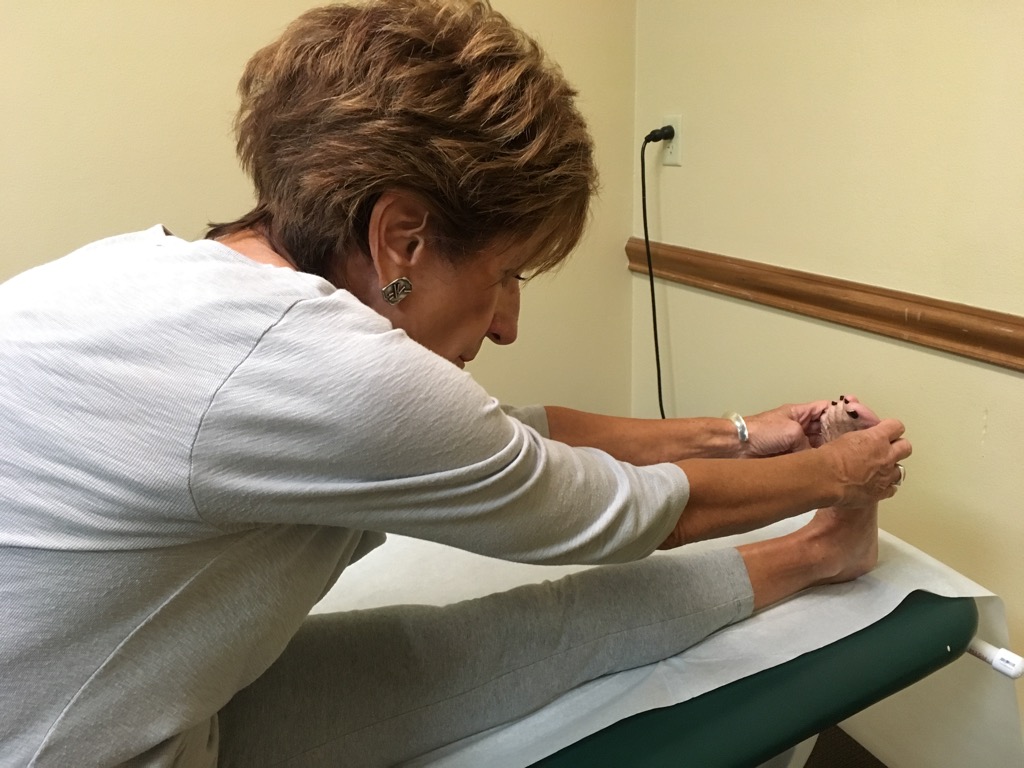 Strengthening lower extremity muscles is important. a method to check lower extremity strength is to kneel down on one leg ,stand back up without difficulty. Repeat with the other leg. If you have difficulty, there is leg weakness, which needs to be strengthened.
Strengthening lower extremity muscles is important. a method to check lower extremity strength is to kneel down on one leg ,stand back up without difficulty. Repeat with the other leg. If you have difficulty, there is leg weakness, which needs to be strengthened.
Lengthening or stretching also is important . Sit on floor or bed with legs straight, bend forward keeping knees flat and grasp the ankles, if unable stretching exercises need to be done.